What The Gold Standard Is Not
There are two important clarifications to make in terms of that what the gold standard is not. The first one has to do with gold standard pegging the price of gold, and the second has to do with the gold standard as an international regime of fixed exchange rates.
The gold standard does not fix the price of gold.
As mentioned above, under a gold standard, gold is what functions as money, the convertible banknotes issued by central banks are money substitutes. Recall that ultimately what functions as the unit of account is gold. This means that the gold standard is not a policy that fixes the price of gold as if central bank banknotes were money and gold just a commodity of reference. This is not just semantics.
When you deposit your dollars into a bank account you receive a checkbook that you can use to write checks that are convertible to dollars. This check is similar to the convertible banknotes that central banks issues. And just as if you write too many checks your bank account balance goes down, if a central bank issues too many convertible banknotes their reserves go down as well. And just as we do not say that we fix the price of the dollar in terms of our checks, we cannot argue that under gold standard we are fixing the price of gold in terms of central bank convertible banknotes.
The gold standard is not a regime of international fixed exchange rates.
Was Abandoning The Gold Standard Successful
U.S. inflation, stagflation, and eroding U.S. wealth have been quelled. United States gold reserves ended at the end of 1980, with the dollar delinking from gold. Its not likely that it wont get rid of its gold currency. Due to the evolution of the world economy since then, the gold standard will return to its former glory.
Which Of The Following Was A Reason That Led To The Collapse Of The Gold Standard In 1973 Quizlet
Which of the following was a reason that led to the collapse of the gold standard in 1973? mismanagement of the US economy. Which of the following refers to a system under which the exchange rate for converting one currency into another is continuously adjusted depending on the laws of supply and demand?
Don’t Miss: Cancel Golds Gym Membership
Did The Gold Standard Cause Deflation
With a closed economy under the gold standard, gold is how the countrys money supply is established. By mining more gold, the government will be able to increase its money supply. The gold supply adversely affects growth in the economy. Deflation and economic growth are reduced by limited gold supply.
What Happened To The Dollar When It Was No Longer Tied To Gold
To prevent a run on Fort Knox, the President thus declared that the nation would no longer exchange dollars for gold. That meant that the dollar was no longer as good as gold. Thus foreigners had to sell their dollars in money markets for whatever they could get. In effect the dollar had been devalued.
Also Check: Free Eagles App
Why Did The Gold Standard Fail
In an unstable and jobless decade, the gold standard was the main source of unemployment and instability during the Great Depression of the 1930s. In 1931, the British government abandoned its Gold standard after gold became less appealing in that countrys economy, the British had no intention of redeeming their currency from this gold.
When Did Germany Abandon The Gold Standard
1910-1914: Following the birth of a central monetary authority in 1876, Germany participates in the prewar gold standard. Monetary policy reflects Germany’s typical concern for controlling inflation until the outbreak of war. 1915-1918: Like most countries, Germany suspends the gold standard for the war.
Don’t Miss: How Much Is A 10k Silver Ring Worth
Why Is Gold In Debate Again
Libertarian Rep. Ron Paul made a return to honest money a key plank of his presidential run, and the idea took hold among Tea Party conservatives outraged over the Federal Reserves loose monetary policies since the financial crisis. They argue that the U.S. debt now exceeds $16 trillion because the government has become too cavalier about borrowing and printing money. When the Fed prints money, gold-standard advocates say, it cheapens the value of a dollar, promotes inflation, and effectively steals money from the citizenry. In a nod to those ideas, the Republican Partys 2012 platform calls for the creation of a commission to investigate setting a fixed value for the dollar. The gold standard forces the U.S. to live within its means, said investment strategist Mark Luschini. Think of it as a person with a debit card rather than a credit card. The debit card holder can only spend what he or she has in the bank.
Years After Nixon Ended The Gold Standard Dollars Dominance Faces Threat
- Order Reprints
- Print Article
President Richard Nixon announcing the severing of links between the dollar and gold as part of a broad economic plan on Aug. 15, 1971.
Fifty years ago this Sunday, President Richard Nixon announced a bold economic plan, including the severing of the U.S. dollars ties to gold. Since then, the worlds monetary system has consisted of freely floating currencies. The dollar nonetheless remains the primary legal tender used internationally for trade, finance, and as a store of value, which has conferred upon the U.S. enormous advantages. Whether that will continue for the next half-century is far from certain.
The Bretton Woods system, in effect back…
You May Like: Selling Gold Dental Crowns
The Stability Of The Classical Gold Standard
The fundamental reason for the stability of the classical gold standard is that there was always absolute private-sector credibility in the commitment to the fixed domestic-currency price of gold on the part of the center country , two of the three remaining core countries, and certain other European countries . Certainly, that was true from the late-1870s onward. In earlier periods, that commitment had a contingency aspect: it was recognized that convertibility could be suspended in the event of dire emergency but, after normal conditions were restored, convertibility would be re-established at the pre-existing mint price and gold contracts would again be honored. The Bank Restriction Period is an example of the proper application of the contingency, as is the greenback period .
Absolute Credibility Meant Zero Convertibility and Exchange Risk
The absolute credibility in countries commitment to convertiblity at the existing mint price implied that there was extremely low, essentially zero, convertibility risk and exchange risk .
Reasons Why Commitment to Convertibility Was So Credible
There were many reasons why the commitment to convertibility was so credible. Contracts were expressed in gold if convertibility were abandoned, contracts would inevitably be violated an undesirable outcome for the monetary authority. Shocks to the domestic and world economies were infrequent and generally mild. There was basically international peace and domestic calm.
: Officer .
Is Money Printed Based On Gold
It was used as a world reserve currency through most of this time. Countries had to back their printed fiat currencies with an equal amount of gold in their reserves. Thus, it limited the printing of fiat currencies. In fact, the United States of America used gold standard up till 1971 after which it was discontinued.
Also Check: Heaviest Credit Card
What Would Happen If The Us Went Back To The Gold Standard
For example, if the US went back to the gold standard and set the price of gold at US$500 per ounce, the value of the dollar would be 1/500th of an ounce of gold. This would offer reliable price stability. By introducing the gold standard, transactions no longer have to be done with heavy gold bullion or gold coins.
What Role Did The Abandonment Of The Gold Standard Play In Bank Holidays

People feared that Roosevelt would abandon the gold standard and reduce the value of the dollar to fight the Depression. … Many Americans and foreign investors with deposits in American banks decided to take their money out of the banks and convert it to gold before it lost its value.
Customer service
Don’t Miss: How Much Is A 400 Oz Gold Bar Worth
Why Did The Us Go Off The Gold Standard In 1971
The Nixon shock was a series of economic measures undertaken by United States President Richard Nixon in 1971, in response to increasing inflation, the most significant of which were wage and price freezes, surcharges on imports, and the unilateral cancellation of the direct international convertibility of the United …
What Was Wrong With The Gold Standard
Although the gold standard brings long-run price stability, it is historically associated with high short-run price volatility. It has been argued by Schwartz, among others, that instability in short-term price levels can lead to financial instability as lenders and borrowers become uncertain about the value of debt.
Recommended Reading: Eiffel Tower Ring Kay Jewelers
Why Not Go Back To The Gold Standard
There are significant problems with tying currency to the gold supply:
- It doesnt guarantee financial or economic stability.
- Its costly and environmentally damaging to mine.
- The supply of gold is not fixed.
The U.S. mines a lot of gold, but were not the biggest producer, Wheelock said. The bigger suppliers of gold would have more control over our monetary policy, and theres no reason to have it because we can get the advantages of the gold standard and avoid the disadvantages without being on a gold standard.
Why Did The Uk Abandon The Gold Standard In 1931
On September 19, 1931, speculative attacks on the pound led the Bank of England to abandon the gold standard, ostensibly “temporarily”. However, the ostensibly temporary departure from the gold standard had unexpectedly positive effects on the economy, leading to greater acceptance of departing from the gold standard.
Read Also: War Thunder Earn Golden Eagles
The Gold Standard: A History
“We have gold because we cannot trust governments,” President Herbert Hoover famously said in 1933 in his statement to Franklin D. Roosevelt. This statement foresaw one of the most draconian events in U.S. financial history: the Emergency Banking Act, which forced all Americans to convert their gold coins, bullion, and certificates into U.S. dollars. While the legislation successfully stopped the outflow of gold during the Great Depression, it did not change the conviction of gold bugs, people who are forever confident in gold’s stability as a source of wealth.
Gold has a history like that of no other asset class in that it has a unique influence on its own supply and demand. Gold bugs still cling to a past when gold was king, but gold’s past also includes a fall that must be understood to properly assess its future.
What President Ended The Gold Standard
President RooseveltOn April 20, President Roosevelt issued a proclamation that formally suspended the gold standard. The proclamation prohibited exports of gold and prohibited the Treasury and financial institutions from converting currency and deposits into gold coins and ingots. The actions halted gold outflows.
Also Check: War Thunder How To Get Golden Eagles
Lawrence H Officer University Of Illinois At Chicago
The gold standard is the most famous monetary system that ever existed. The periods in which the gold standard flourished, the groupings of countries under the gold standard, and the dates during which individual countries adhered to this standard are delineated in the first section. Then characteristics of the gold standard , the various types of the standard , and implications for the money supply of a country on the standard are outlined. The longest section is devoted to the classical gold standard, the predominant monetary system that ended in 1914 , followed by a section on the interwar gold standard, which operated between the two World Wars .
What Are The Disadvantages Of The Gold Standard

The disadvantages are that it may not provide sufficient flexibility in the supply of money, because the supply of newly mined gold is not closely related to the growing needs of the world economy for a commensurate supply of money, a country may not be able to isolate its economy from depression or inflation
Also Check: Rs Gold Sell
Countries And Dates On The Gold Standard
Countries on the gold standard and the periods during which they were on gold are listed in Tables 1 and 2 for the classical and interwar gold standards. Types of gold standard, ambiguities of dates, and individual-country cases are considered in later sections. The country groupings reflect the importance of countries to establishment and maintenance of the standard. Center countries Britain in the classical standard, the United Kingdom and the United States in the interwar period were indispensable to the spread and functioning of the gold standard. Along with the other core countries France and Germany, and the United States in the classical period they attracted other countries to adopt the gold standard, in particular, British colonies and dominions, Western European countries, and Scandinavia. Other countries and, for some purposes, also British colonies and dominions were in the periphery: acted on, rather than actors, in the gold-standard eras, and generally not as committed to the gold standard.
| Table 1Countries on Classical Gold Standard | |
| Country | |
| Exchange | 1889p-1914 |
: Bloomfield , Bordo and Kydland , Bordo and Schwartz , Brown , Bureau of the Mint , de Cecco , Ding , Director of the Mint , Ford , Gallarotti , Gunasekera , Hawtrey , Hershlag , Ingram , Kemmerer , Kindleberger , Lampe , MacKay , MacLeod , Norman , Officer , Pamuk , Powell , Rifaat , Shinjo , Spalding , Wallich , Yeager , Young .
| Table 2Countries on Interwar Gold Standard |
| Country |
| 1930 |
Experiences From The Napoleonic Wars
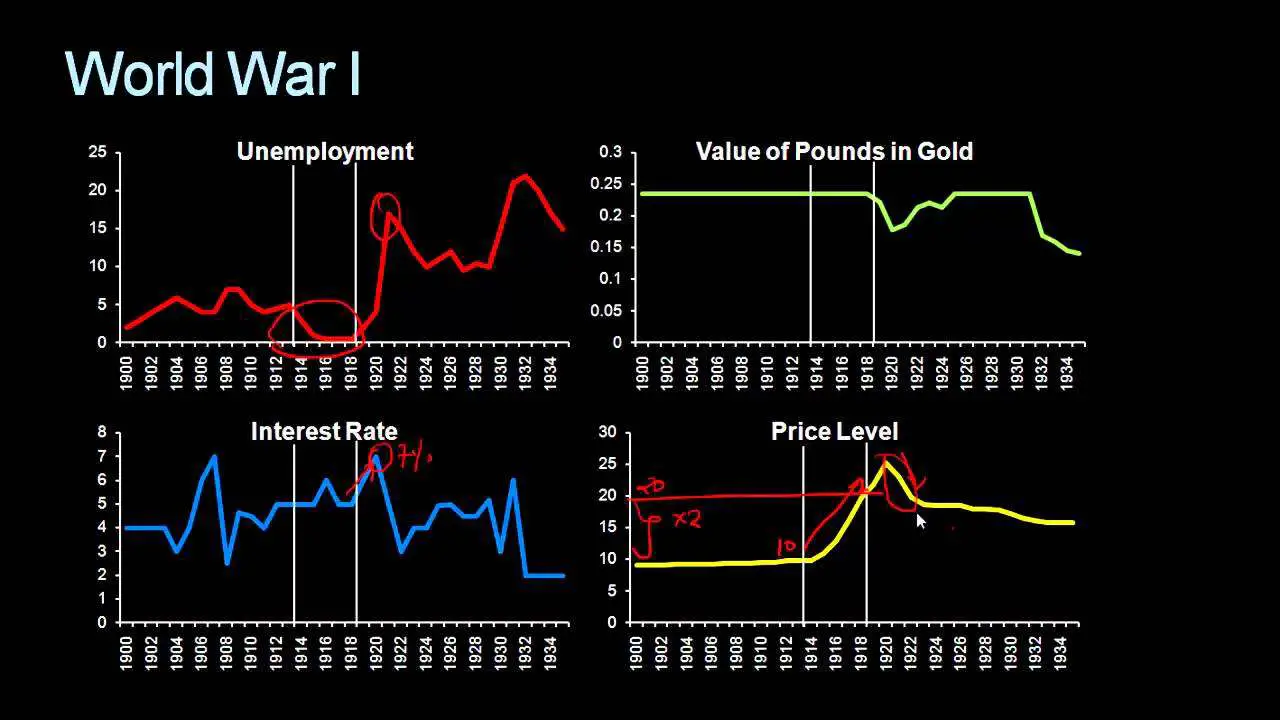
Now at this point the British central bank thought it was extremely important that Britain eventually return to the gold standard. The reason they thought it was important is because they were thinking of Britains experiences a hundred years prior to WWI. During the Napoleonic war Britain had done something very similar to what they had done during WWI. While they have been fighting the war with Napoleon they had doubled the money supply in the economy, thereby doubling prices. After the war was over they decided to return to the gold standard by increasing interest rates so as to contract the money supply back to the level it was at before the war. It was extremely painful to contract the money supply because it resulted in a million people being put out of work, but after Britain was back on the gold standard they were rewarded by about fifty or sixty years of prosperity. The British central bank tried to recreate this experience after WWI and that is why they felt that it was imperative that Britain return to the gold standard.
Read Also: Gold Rush Season 10 Release Date
Fdr Takes United States Off Gold Standard
On June 5, 1933, the United States went off the gold standard, a monetary system in which currency is backed by gold, when Congress enacted a joint resolution nullifying the right of creditors to demand payment in gold. The United States had been on a gold standard since 1879, except for an embargo on gold exports during World War I, but bank failures during the Great Depression of the 1930s frightened the public into hoarding gold, making the policy untenable.
Soon after taking office in March 1933, President Roosevelt declared a nationwide bank moratorium in order to prevent a run on the banks by consumers lacking confidence in the economy. He also forbade banks to pay out gold or to export it. According to Keynesian economic theory, one of the best ways to fight off an economic downturn is to inflate the money supply. And increasing the amount of gold held by the Federal Reserve would in turn increase its power to inflate the money supply. Facing similar pressures, Britain had dropped the gold standard in 1931, and Roosevelt had taken note.
READ MORE: How Did the Gold Standard Contribute to the Great Depression?
The government held the $35 per ounce price until August 15, 1971, when President Richard Nixon announced that the United States would no longer convert dollars to gold at a fixed value, thus completely abandoning the gold standard. In 1974, President Gerald Ford signed legislation that permitted Americans again to own gold bullion.
Instability Of The Interwar Gold Standard
The features that fostered stability of the classical gold standard did not apply to the interwar standard instead, many forces made for instability. The process of establishing fixed exchange rates was piecemeal and haphazard, resulting in disequilibrium exchange rates. The United Kingdom restored convertibility at the prewar mint price without sufficient deflation, resulting in an overvalued currency of about ten percent. . A depressed export sector and chronic balance-of-payments difficulties were to result. Other overvalued currencies were those of Denmark, Italy, and Norway. In contrast, France, Germany, and Belgium had undervalued currencies. Wages and prices were less flexible than in the prewar period. In particular, powerful unions kept wages and unemployment high in British export industries, hindering balance-of-payments correction.
Higher trade barriers than prewar also restrained adjustment.
In the classical period, London was the one dominant financial center in the interwar period it was joined by New York and, in the late 1920s, Paris. Both private and official holdings of foreign currency could shift among the two or three centers, as interest-rate differentials and confidence levels changed.
The Bank of England did not provide a leadership role in any important way, and central-bank cooperation was insufficient to establish credibility in the commitment to currency convertibility.
Don’t Miss: Runescapegoldmarket
